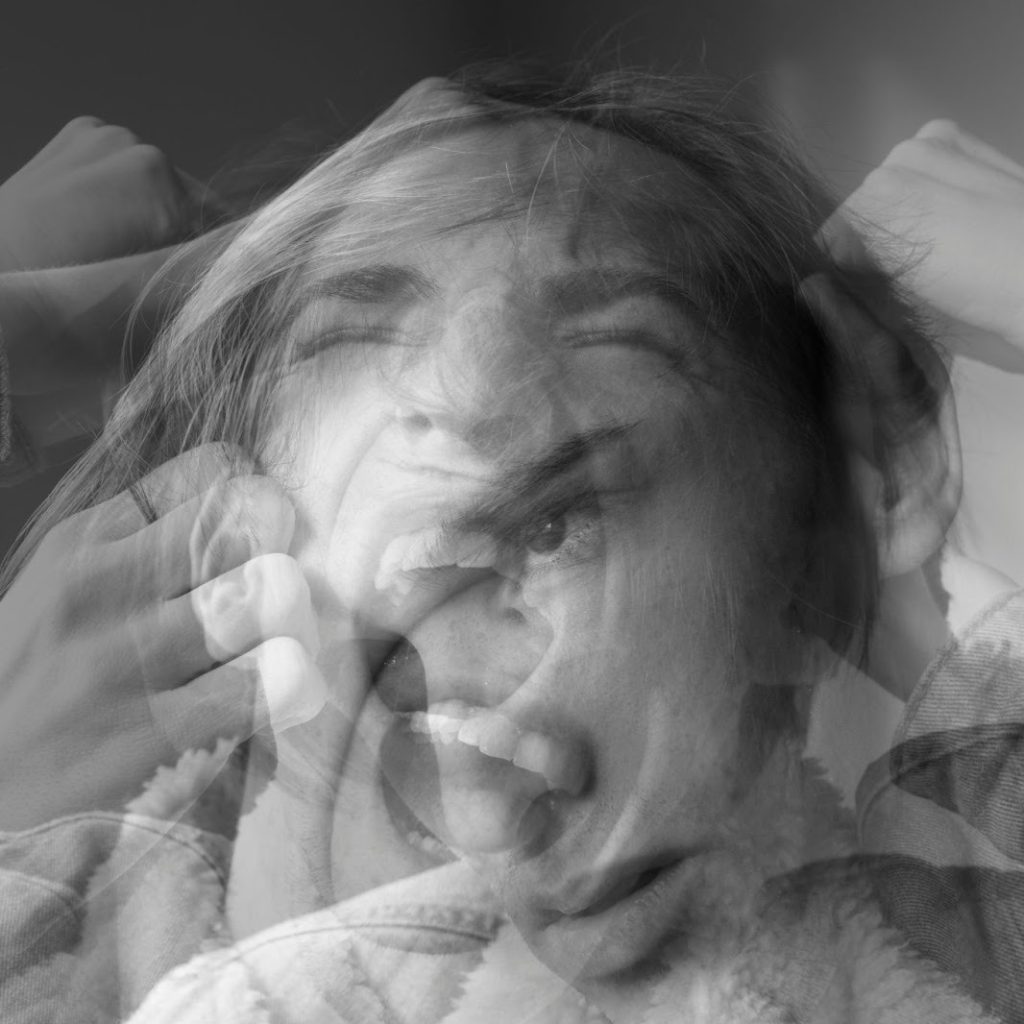
Imagine standing in your kitchen, washing your hands repeatedly, convinced that something terrible will happen if you stop. Or lying awake at night, trapped in a cycle of thoughts you can’t control. For millions of people worldwide, this is the daily reality of living with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD).
OCD is more than just being “a little tidy” or “organized.” It’s a mental health condition marked by intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) that can disrupt everyday life, relationships and overall well-being.
In this guide, we’ll explore OCD symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment and coping strategies, helping you understand and manage this complex disorder.
What is OCD? Symptoms and Signs You Should Know
OCD can manifest as obsessions, compulsions or both. Obsessions are recurrent thoughts, urges or mental pictorials that are intrusive, undesirable and cause most individuals to be anxious.
Common obsessions include:
- Fear of contamination or germs.
- Worrying about losing or misplacing things
- Concern about losing control over actions or impulses
- Violent or unwanted thoughts about yourself or others
- Taboo or forbidden thoughts related to sex, religion or harm
- Urges for perfection, balance, or symmetry
Compulsions refer to the repetitive actions that one is compelled to perform, usually as a result of an obsession. Common compulsions include:
- Excessive cleaning or hand-washing
- Organizing or arranging items precisely
- Repeatedly checking things like doors or ovens
- Counting, tapping, or repeating words
- Motor or vocal tics (e.g., blinking, grimacing, throat-clearing)
Causes of OCD: Why It Happens
The exact cause of OCD is unknown, but research points to a combination of genetic, neurological, and environmental factors:
- Genetics: OCD can run in families, suggesting a hereditary link.
- Brain chemistry: An imbalance in serotonin, a neurotransmitter important for mood and behavior, may contribute to OCD symptoms.
- Brain structure: Increased activity in the frontal lobes and basal ganglia, which are involved in decision-making and habit formation, may make it harder to control repetitive thoughts and actions.
- Stress and trauma: Life events or prolonged stress can trigger or worsen OCD symptoms.
Diagnosis of OCD
OCD diagnosis usually involves a thorough evaluation by a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist. This may include a detailed interviews about symptoms, their duration and severity.
Cognitive-behavioral assessments or neuropsychological testing. Observing how obsessions and compulsions affect daily life. A correct diagnosis is essential to create a personalized treatment plan.
OCD Treatment: Therapy, Medication, and Support
While OCD can be challenging, evidence-based treatments can help manage symptoms.
Therapies
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT):
CBT helps individuals identify harmful or unrealistic thoughts and respond differently. By challenging negative thought patterns, patients can regain control over their behavior.
- Exposure and response prevention therapy (ERP):
A specialized form of CBT, ERP gradually exposes individuals to situations that trigger obsessions (like touching a “contaminated” object) while preventing the compulsive response (like hand-washing). Over time, this reduces the anxiety and need for rituals.
Medication
Antidepressants, particularly Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), can help regulate serotonin levels and reduce OCD symptoms. These medications may take 8–12 weeks to show effect and are often combined with therapy for best results.
Coping Strategies for Managing OCD
Even with treatment, OCD can be exhausting. Some practical strategies to manage symptoms include:
- Mindfulness: Learning to observe intrusive thoughts without acting on them
- Relaxation exercises: Deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation
- Support systems: Connecting with friends, family, or OCD support groups
- Lifestyle adjustments: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and consistent routines
Living with OCD: Challenges and Impact
OCD can make everyday tasks overwhelming—shopping, cooking, or even leaving the house can feel impossible. The emotional toll is real: frustration, shame, and isolation often accompany the disorder.
Yet, with proper treatment and support, many individuals find ways to regain control and lead fulfilling lives. Every small step forward—resisting a compulsion, challenging an obsession—is a victory worth acknowledging.
Conclusion: Hope and Healing
OCD affects each person differently. For some, therapy or medication may effectively control symptoms. For others, it may be a lifelong challenge that requires ongoing management.
If you or a loved one struggles with OCD, remember: help is available, understanding is possible and healing begins with awareness and action.
“Living with OCD is hard, but you are not alone, and progress is always possible.”
References
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
- National Institute of Mental Health. (2023). Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/obsessive-compulsive-disorder-ocd
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/obsessive-compulsive-disorder/symptoms-causes/syc-20354432
- Fineberg, N. A., Reghunandanan, S., Brown, A., & Pampaloni, I. (2013). Pharmacotherapy of obsessive-compulsive disorder: Evidence-based treatment and beyond. World Journal of Biological Psychiatry, 14(2), 119–145. https://doi.org/10.3109/15622975.2012.739652
- Abramowitz, J. S., McKay, D., & Storch, E. A. (2017). The Wiley handbook of obsessive-compulsive disorders. John Wiley & Sons.